In-situ detection technique for charge transfer behavior of direct Z-scheme BiVO4/UiO-66-NH2 composites during photocatalytic thioanisole conversion
摘要
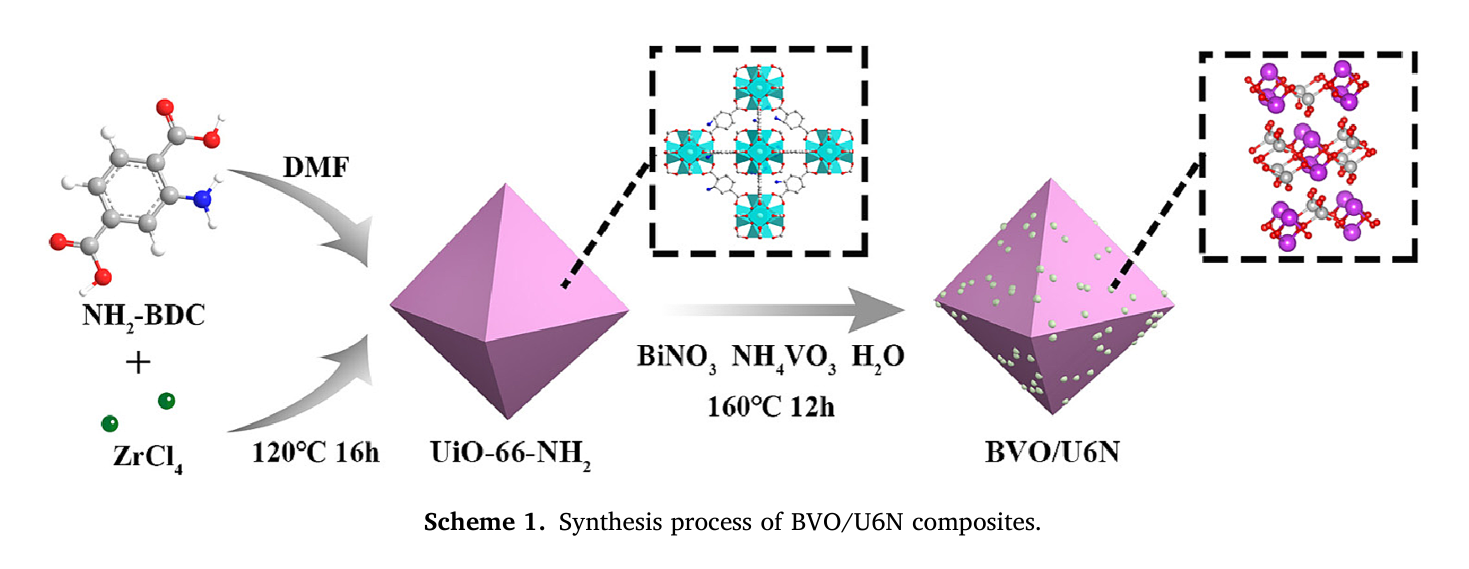
The photocatalytic efficiency can be enhanced by constructing Z-scheme heterostructures. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive and direct evidence regarding the charge transfer pathway and mode during the photocatalytic process. A composite photocatalyst BiVO4/UiO-66-NH2 (BVO/U6N) was prepared by in-situ loading BiVO4 nanoparticles onto the surface of UiO-66-NH2 using a hydrothermal method. This catalyst effectively promotes the photocatalytic conversion of thioanisole to sulfoxide. The differences between BiVO4 and UiO-66-NH2 in band structure and Fermi energy level enable the composite to act according to the Z-scheme charge transfer pattern, which significantly enhances charge separation efficiency. In-situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (in-situ XPS) combined with DFT calculation confirmed the transfer of electrons from UiO-66-NH2 to BiVO4, driven by an internal electric field (IEF) upon hybridization. This demonstrates the formation of a Z-scheme photogenerated charge transfer pathway in the BVO/U6N composite. The direct Z-scheme system significantly enhances the carrier redox, resulting in a sulfoxide yield of 95.21% for the optimized sample in methanol, which is 5 times and 4.1 times higher than that of UiO-66-NH2 and BiVO4, respectively. BVO/U6N exhibits efficient photocatalysis and selectivity towards various substrate sulfides, making it a highly promising heterogeneous photocatalyst.